 Is Alcohol a Stimulant?
Is Alcohol a Stimulant?Is alcohol stimulating? It is common knowledge that alcohol affects your brain function, but you can ask yourself exactly how it works. Some people think of alcohol as a stimulant that can increase their heart rate, give it energy and decrease their inhibitions. However, this is not the whole story. Alcohol has some initial stimulant effects, but it is mainly a depressive, which means it delays your body. How it affects you depends on your body chemistry, how much alcohol you ingest at once and your alcohol tolerance. This article reviews the effects of alcohol, both stimulating and depressive. Stimulants and depressants affect both your nervous system and brain function, although in opposite way. Stimulants excite your nervous system. They can increase blood pressure and heart rate and . In high doses, they can cause insomnia and make you jittery and impulsive (). Examples of stimulants include mild, such as caffeine, as well as stronger prescription amphetamines or illicit drugs such as cocaine. On the other hand, depressants slow you down by decreasing heart rate and blood pressure. They can help you and, at the end end, completely sedate (). Benzodiazepines are a class of depressive drugs used to treat insomnia and anxiety, while prescription opiates are powerful products in this category. Some compounds may have features of both. Examples include nicotine, although it is more frequently characterized as stimulant, and alcohol, which is mainly depressive but has some stimulating effects (, ). You should not mix alcohol and stimulant or depressive drugs due to the risk of serious side effects. SummaryStimulants excite your nervous system and can increase your energy, while depressants slow down your nervous system and relax it. Some substances have stimulant and depressive effects. Stimulants excite your nervous system and can increase your energy, while depressants slow down your nervous system and relax it. Some substances have stimulant and depressive effects. The initial doses of alcohol indicate your brain to release, the so-called "happy hormone", which may cause you to feel stimulated and energized (). In addition, alcohol can increase your heart rate and can lead to greater aggression in some individuals, both typical of stimulants. Stimulant effects occur when your (BAC) approaches 0.05 mg/L but are replaced by more depressive effects once your BAC reaches 0.08 mg/L, the level at which you consider yourself legally disabled to drive in most areas of the United States (). One important thing is that the effects of alcohol vary a lot by individual and are influenced by several factors, including body chemistry, sex, weight, alcohol tolerance and the dose of alcohol consumed. To get a rough understanding of how many drinks would lead you to these BAC levels, there are many calculators available online. In addition, some people may experience more alcohol-stimulating effects, while others may experience more depressive effects. Researchers theorize that people who experience more stimulating effects and less sedative effects are at increased risk of alcoholism (). However, while it has some stimulant effects, especially at low doses, alcohol is primarily a depressive substance. AbstractAlcohol has an initial stimulant effect in lower doses. It can increase your heart rate, aggression and impulsivity, as well as cause an increase in dopamine levels. Alcohol has an initial stimulant effect on lower doses. It can increase your heart rate, aggression and impulsivity, as well as cause an increase in dopamine levels. After initial stimulant effects, alcohol decreases the central nervous system, decreasing blood pressure, heart rate and mental clarity (). In turn, people who have ingested have slower reaction times and may seem sleepy, disoriented or sedated. In addition, higher doses of alcohol can suppress the production of dopamine, which can make it feel sad or unlisted (). Alcohol depressive effects occur when BAC reaches about 0.08 mg/L. Once your BAC reaches 0.2 mg/l or greater, your depressive effects on your respiratory system can become so powerful that they cause coma or death (). Abstract In larger quantities, alcohol changes from a stimulant to a depressive. It reduces your nervous system, blood pressure and heart rate, leading to lack of mental sleepiness and lack of coordination. In larger quantities, alcohol changes from a stimulant to a depressive. It reduces your nervous system, blood pressure and heart rate, leading to lack of mental sleepiness and lack of coordination. Alcohol is a depressive with some stimulating effects. In small doses, you can increase your heart rate, aggression and impulsivity. However, in larger doses, alcohol usually causes lazy, disorientation, and slower reaction times, as it decreases mental acuity, blood pressure and heart rate. It personally depends on your body chemistry, how much you drink and your alcohol tolerance. Note that when it comes to alcohol, moderation is key to avoiding negative health effects. The moderate drink is defined as one and two drinks a day for women and men, respectively (). Last medical review on January 16, 2020Read this following
PodcastsPublications Is ALCOHOL a powerful? Until recently, alcohol was considered a respiratory and heart stimulant. Whiskey was probably the most popular domestic remedy for such occasional alterations as fainting, in which stimulation was presumably required. The popular idea that alcohol is a tone stimulant has so often proved to be untenable on the basis of scientific evidence that it seems almost superfluous to refute the wrong notion again. No one will deny that a sense of relief often follows the use of alcohol in conditions where stimulation appears to be indicated. In such cases, however, it has been shown to act merely as an irritant for mucous membranes of the mouth and throat, thus promoting a local benefic reaction before alcohol has had time to be absorbed and stimulated in any way the depressed function. There would be no occasion to revert to the subject at this time. Is subpoena always a stimulant? JAMA. 1919;73(26):1940-1941. doi:10.1001/jama.1919.02610520030018Download Appointments Archive:© 2021 Others I also like Select your interests Customize your JAMA Network Experience by selecting one or more items from the list below. JAMAContentPodcastsJournal InformationSubscribeJAMA NetworkPublications SitesSpecial Communication BlogsInformation ForJAMA Network ProductsJN LearningHelpJAMA Career Center © 2021 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Silence Silence Log in to access your subscriptions Purchase access Sign in to download free article PDFsSign in to access your subscriptions Create a personal account or log in to: Sign in to access your subscriptions Purchase access Log in to save your search Log in to log in to save your search Log in to save your search Access to purchase Log in to customize your interests Create a personal account or log in to:

Is Alcohol a Depressant or a Stimulant? - PAX Memphis Recovery Center
Is alcohol a stimulant? » Ask Our Doctors (by JourneyPure)
Is Alcohol a Stimulant? - Stonegate Center
Is Alcohol a Depressant or a Stimulant? - PAX Memphis Recovery Center
Is Alcohol a Depressant and How Does it Affect your Brain? - The Liberty Ranch
Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant? | Sagebrush Treatment Centers
Is alcohol a stimulant? » Ask Our Doctors (by JourneyPure)
Is Alcohol a Depressant? - Depressants - Addiction Center
Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant? - Level Up Lake Worth
What Are the Adverse Side Effects of Mixing Alcohol & Drugs?
Is Alcohol a Stimulant? - Stonegate Center
Is Alcohol A Stimulant? – A Closer Look | Experience Ibogaine Treatment Center
Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant? | Houston Alcohol Addiction Rehab
Is Alcohol a Stimulant? Or is it a Depressant? Effects on the Brain
Is Alcohol a Stimulant or a Depressant? - Healthy Life Recovery
Initial stimulant, rewarding effects predict heavy alcohol use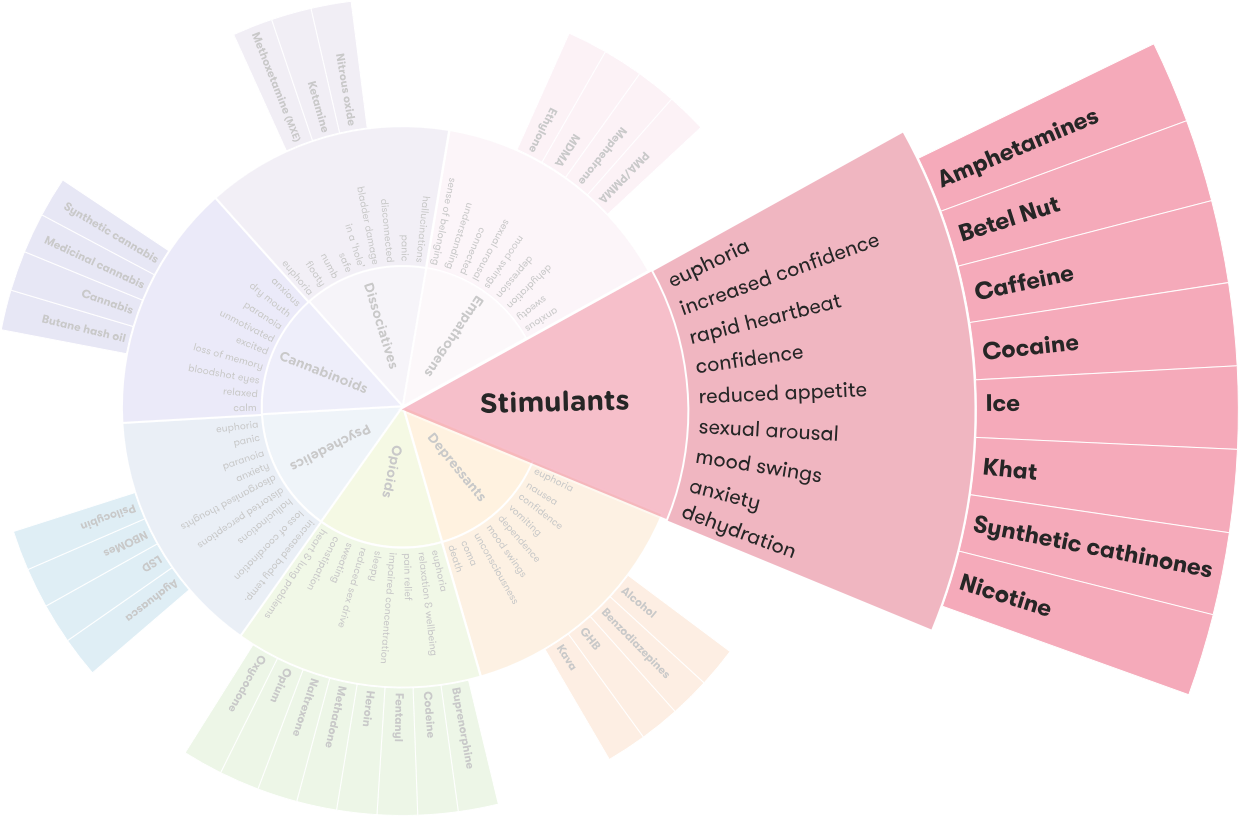
Stimulants - Alcohol and Drug Foundation
Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant? - Compass Detox
How Alcohol Effects Us: The Biphasic Curve Shows the Pleasure vs Pain Relationship
Drug Effects on Developing Brains - Teens | Sandstone Care
Is Alcohol A Stimulant? | Crestview Recovery Center
Alcoholism of Human
Depressants – Northwest Regional Drug & Alcohol Task Force
Management of Drug and Alcohol Withdrawal | NEJM
is alcohol a stimulant or depressant Tag Archives | Atlanta Detox Center
IS ALCOHOL A STIMULANT OR A DEPRESSANT? - Spiritsfully
Drugs and Consciousness | Introduction to Psychology
What Are the Adverse Side Effects of Mixing Alcohol & Drugs?
Assessing the stimulant effects of alcohol in humans - ScienceDirect
Is Alcohol A Stimulant? | Just Believe Detox
Is Alcohol a Stimulant? - Stonegate Center
Spectrum of use – not necessarily daily use. What is the legal age for consuming alcohol? Why? The myelin sheath encompassing the brain reaches it's. - ppt download
Alcohol consumption, stimulant use, folic acid supplementation and... | Download Scientific Diagram
Is Alcohol A Stimulant? | Addiction Treatment Center San Antonio TX
Is Alcohol a Stimulant? Learn the Truth | Serenity Lodge Lake Arrowhead
Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant? | Banyan Palm Springs
How Alcohol Effects Us: The Biphasic Curve Shows the Pleasure vs Pain Relationship
IS ALCOHOL A STIMULANT OR A DEPRESSANT? - Spiritsfully
Stimulants and Alcohol: Mixing Ethanol With Cocaine Or Amphetamines
 Is Alcohol a Stimulant?
Is Alcohol a Stimulant?



































Posting Komentar untuk "is alcohol a stimulant"