 Researchers examine unusual condition of mirror-touch synesthesia
Researchers examine unusual condition of mirror-touch synesthesiaSynesthesia of the mirror touchThe synesthesia of the mirror touch is a rare condition that makes individuals experience a similar sensation in the same or opposite part of the body (like the touch) that another person feels. For example, if someone with this condition watched someone touching their , they would feel the same in their own cheek. , in general, is described as a condition in which an individual causes to experience an additional sensation. Synesthesia is generally a development condition; however, it has recently shown that the mirror touch synesthesia can be acquired after the next sensory loss. Mirror synesthesia The severity of the condition varies from person to person. Some individuals have intense synthetic physical responses to any physical touch they see, while others describe their experiences as feeling an "eco" of the touch they see. This seems to be comparable to the distinctions found in other forms of synesthesia. In addition, some mirror-touch synthesis feel the phenomenon only in response to other human beings who touch, while others also perceive it when they touch animals or even inanimate objects. The synesthesia of the mirror is approximately 1.6–2.5% of the general population. Mirror touch synthesis has higher levels and those who do not have the condition, although they differ from person to person. Your emotional experience of the observed touch may differ from the emotional experience of the touching person (a pleasant touch may be perceived as unpleasant or vice versa). The synesthesia of the mirror touch can also co-curate with . ContentIntroduction[] Three conditions must be met to confirm the presence of mirror touch. To examine the situation, a study was conducted at University College London and at the University of Sussex. 567 undergraduate participants were recruited and a . The questionnaire was determined that approximately 2.5% of the population experienced symptoms of mirror-touch synesthesia. Other studies have shown that the prevalence is 1.6%, which means that this condition is one of the most common types of synesthesesia, along with (1.4%) and day sinesthesia (2.8%). At this time it is believed that there are two subtypes of the condition. The first type makes a person feel by his body that reflects the observed touch. The second type makes a person feel sensations on the same side of his body as the observed touch. Studies have tried to define more explicitly the synthetic responses. In most studies, participants are asked to observe someone else who is being touched and to report what kind of synthetic response they experience. In a particular case, clips were used to show different types of observed touch. The synesthetic touch is not affected by the location of the observed touch (arma, leg, hand, etc.); however, it is sometimes affected by the spatial orientation of the observed touch. When the cross hands are touched, the hands crumble in the syntheses. However, when the observed hand is backwards, the observed touch is not turned. The intensity is not affected either if the observed act consists of someone touching them, against someone who touches them. In addition, the type of object that makes the touch has a significant effect on the intensity of the response. If a finger or knife tip is used, a much higher intensity is experienced than if used. Finally, seeing a touched doll significantly decreases the intensity of the observed touch. For this reason, it is suspected that to experience a synesthetic touch, the syntheses must observe someone who is capable of feeling sensations. Mirror tactile responses are not limited to feeling touch. Mirror touch synthesizers have a higher capacity to feel that non-synthes, and therefore can feel the same emotions as someone else can be observed to feel. In addition, some individuals experience pain by observing someone else with pain, and this is a condition generally developed from birth. Approximately 30% of the normal population experience some form of this condition and about 16% of the amplifiers report synesthetic pain after a . This condition can be acquired or developed. In the condition, it synthesizes the pain in the same location as the pain observed; however, in the acquired condition, the pain of high intensity is felt in the same location as the trauma. Reported cases[]The first reported case of mirror tactile synesthesia occurred in 2004 in a patient named C. By observing someone else who touched herself, she would also experience the same touch on her body. Although he had experienced this feeling for his entire life, he did not realize that he was abnormal until someone else was informed. He was a healthy person otherwise. After realizing that his perception was abnormal, he realized that his first, also a female, also has mirror touch synes, suggesting that it could be genetic. Required cases[] A male patient, called D.N., suffered one and experimented along with the loss of feeling on the left side of his body. If the stimuli were hidden from his sight, he could not feel any sensation. However, when he could visualize stimuli, he would be able to feel it. Even if D.N. believed he was being touched, he would feel the stimuli. One was carried out in it where he saw a left arm that was touched and was told that it was a real-time video of his left arm that was touched. Although no one touched it, D.N. still experienced sensations where he saw his arm being stimulated in the video. It has been suggested that the symptoms of the synesthesia of the mirror touch may occur in amputates. 98% of amputated people report ghost sensations in their amputated limb, and one of the treatments studied for pain has implied a . In this treatment, the amputate places his good arm in a mirror box, allowing the arm to reflect where the amputated arm would normally be. When the touch is applied to the good arm, amputies have reported corresponding sensations in their ghost limb. These cases can be considered synesthesia of mirror touch because a visual stimulus was able to cause a touch sensation. The studies have studied more thoroughly to determine whether amputies actually experience mirror touch synesesthesia. Four amputees were recruited into a study and asked to observe the arm of an assistant that was touched at various angles. 61 of the 64 trials experienced feelings of mirror touch, and when the arm was tight, the sensations were improved. Finally, an amputee experienced a cold sensation when observing ice cubes touching the assistant's arm. Although there is evidence that the synesthesia of mirror touch occurs in amplifiers, recent data have been inconclusive. Possible mechanisms[]Unethical subjects[] ] In most people, several parts of the brain are activated by observing the touch, especially in the . they play a role in helping to perceive the action. Studies in monkeys have shown that mirror neurons in the ventral fire both when monkeys perform tasks and when monkeys see other monkeys performing the same task. Although the discovery of mirror neurons was made in recent monos studies have suggested that a similar mirror system works in humans. In addition, it has been shown that the mirror system is selective only for biological actions. When observing another human holding an object, there is an increase in the activation of the premotor cortex. However, seeing a robot grab an object, there is no such increase. Below is a list of regions where more activation was observed: The , Bilateral SI and IBS, premotor cortex, and is usually activated when observing the touch to the head or neck of another person. In particular, the visual presentation of faces activates the and . As in the premotor cortex, the activation in these areas is greater when biological actions are observed, or actions carried out by another human. Activation in S1 was organized somatotically, which means that it was organized according to the body part was being touched. Finally, when observing the left-hand touch of a face or human neck, the right SI is activated and when observing the right-hand touch of a face or human neck, the left SI is activated. In symesthesias of mirror touch[]There are three main theories for the presence of mirror-touch synesthesy. The first theory states that the somatosensory mirror system, which modulates the observed touch and the sense touch, has activations that are below a particular threshold in normal people. When the activations are below this threshold, a person can perceive and understand the observed touch. It is suggested that mirror touch synesthesia occurs when this threshold is exceeded. This results in synthesists believing that the touch actually occurs in their own body. Most data support this theory. In general, SI and IBS activations are significantly higher in syntheses than in non-synesthetes. There is also a significantly greater activation in the premotor cortex. It is also suspected that there is an area of the brain that is only activated in syntheses of mirror touch when observing the touch, but not in the non-synesthetes. Studies have shown that the previous insula is performed in mirror tactile syntheses, but it is not activated in non-synestes, when observing the touch. It is believed that the previous insulate mediates the awareness of the touch and is involved in self-processing. The second theory proposes that visual synthesis and in people with mirror touch synesthesia are connected directly in such a way that it is unique to these syntheses. If this is true, then it would not be necessary to say that the same mechanisms involved in the synesthesia of mirror touch are used in the non-syntheses. The third theory involves bimodal cells in the , specifically in the . It is suggested that, when observing the touch, bimodal cells for visual and tactile stimuli are activated above a certain threshold. Verifying his presence in research studies[ ] Most of the studies on the mirror's touch synestheses verify the existence of the condition through a variety of methods. One way is through a sensory interference task. In these tasks, participants are touched on their left cheek, right cheek or not, and are asked to observe a touching assistant. In congruent studies, the attendee is touched in the same location as the participant is touched. In incongruent studies, participants are touched in areas different from those of the assistant. Next, subjects are asked to report where they feel the feeling. For some participants, if the observed touch occurs on the right cheek, they feel a synesthetic touch on their left cheek, and this is called speculation correspondence. If the synthetic touch sits on your right cheek, it is called anatomical correspondence. Most cases of mirror tactile synesthesia include speculative correspondence. The error rate is calculated and a higher rate of error is expected in synthetic matters compared to non-systemic subjects. Link to empathy[ The studies have hypothesized that empathy is experienced by a process of . When we see someone who feels happy, the same neuronal circuits used to make them feel happy are activated in our brain. Since the mirror tactile synthesizers have increased the activation of mirror systems, it seemed likely that they would also experience greater empathy, and this has been confirmed. The mirror touch synthesizes more empathy than the non-syntheses. This was determined using the , which has three main scales: cognitive empathy, emotional reactivity, and . Mirror touch synthesizers showed significantly higher empathy quotient scores in emotional reactivity than in controls. However, the syntheses did not show higher scores in cognitive empathy and social skills. Thus, empathy is multifaceted, and the touch mirror system may not be fully responsible for the ability to empathy. Other ways to investigate the role of the mirror neuron system in empathy have been through pain and . With regard to pain, when painful stimuli are applied to the hands of subjects, neurons in the discharge. Similarly, when painful stimuli are observed that apply to the hands of another person, the same shot. It was also activated by observing people who would be painfully stimulated at a later time. Therefore, the brain areas responsible for responding to pain are activated while experiencing pain, observing someone else experience pain and observing someone who would experience pain at a later time. The , which is activated after a person experiences dislike, is also activated when he observes faces that express dislike, and the intensity of the interaction is directly proportional to the level of repugnance in the observed face. Finally, the inability to experience leads to the deficiency of the ability to recognize the same emotions in others. Patients with brain injuries that prevent them from experiencing disgust cannot recognize the disgust in the faces of others. References[]192ab49ababcd10112ab202abcdef128ab221 Navigation menu Personal tools Named spaces Variants Views More Search Navigation Contributed Tools Printing/exporting Languages
GoogleI'm sorry... Google Sorry... but your computer or network can send automated queries. To protect our users, we cannot process your request right now.

Influence of the body schema on mirror-touch synesthesia - ScienceDirect
Mirror-touch synesthesia | UDaily
Influence of the body schema on mirror-touch synesthesia - ScienceDirect
Mirror-Touch and Mirror-Pain Synesthesia - Reasons for Empathy?
Mirror Touch Synesthesia: Definition, Signs, and How to Cope![PDF] Influence of the body schema on mirror-touch synesthesia | Semantic Scholar PDF] Influence of the body schema on mirror-touch synesthesia | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/15f3c5fab54d3010ec9ad9aff5199fa95e429181/9-Figure5-1.png)
PDF] Influence of the body schema on mirror-touch synesthesia | Semantic Scholar
Mirror-touch synesthesia allows this doctor to have more empathy for his patients — Quartz
Six Lessons About Mirror-Touch Synesthesia From Dr. Joel Salinas - Pacific Standard
People With This Condition Literally Feel What Others Are Feeling | HuffPost Life
What Is Mirror Touch Synesthesia? | Betterhelp
Meet a Doctor With the Almost-Superpower of Mirror-Touch Synesthesia
What I See, I Feel: Mirror-Touch Synesthesia and Empathy | WIRED
Mirror-touch Synesthesia – Brainy
I literally feel your pain': what life's like with mirror-touch synesthesia - BBC Three
Mirror Touch Synesthesia | Causes | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Coping Techniques
Mirror Touch Synesthesia Article on SVA Portfolios | Touch, Portfolios, Mirror
Mirrored Touch Synaesthesia? | Chicago Med - YouTube
Feeling All the Feels: Living With Mirror-Touch Synesthesia - YouTube
Performance of mirror-touch synesthetes and nonsynesthetes on the films... | Download Scientific Diagram
mirror touch synesthesia - YouTube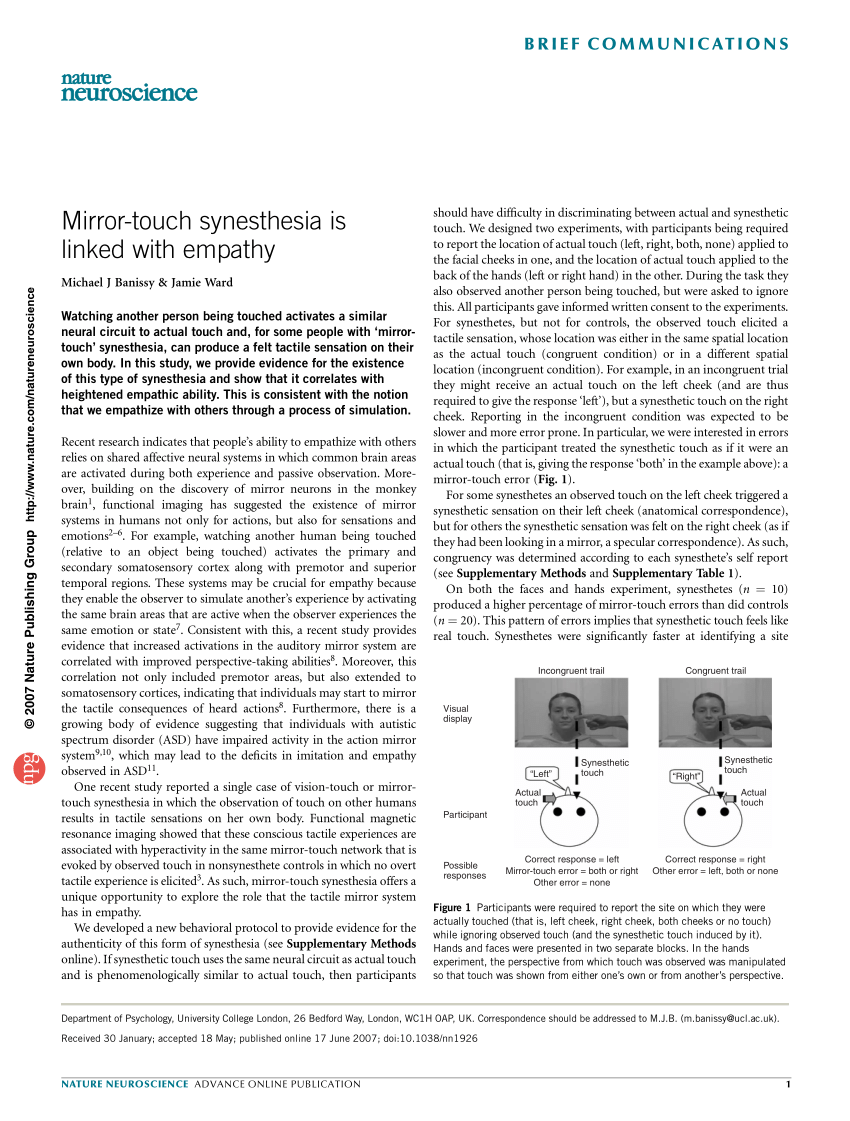
PDF) Mirror-touch synesthesia is linked with empathy
Mirror-Touch Synesthesia - Photos | Facebook
Mirror Touch Synesthesia and the Genetics of Synesthesia | Neuroamer
Mirror-touch synaesthesia in the phantom limbs of amputees - ScienceDirect
Synesthesia: A Disorder That Blurs the Senses - WSJ
Mirror-touch synesthesia
What Is Mirror Touch Synesthesia? | Betterhelp
The Doctor Who Can Feel Peoples' Pain Is Teaching Us About Empathy
Mirror-Touch Synaesthesia Is Not Associated with Heightened Empathy, and Can Occur with Autism
Mirror-touch Synesthesia by Annabelle Schwartz
Acquired Synesthesia - Neurowiki 2014
Mirror Touch Synesthesia and the Genetics of Synesthesia | Neuroamer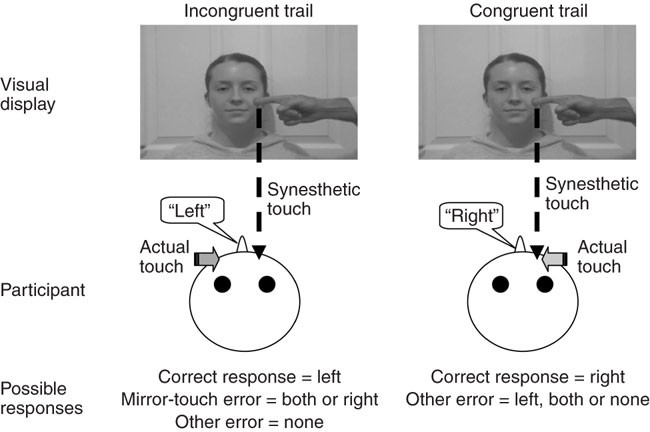
Mirror-touch synesthesia is linked with empathy | Nature Neuroscience
bookofjoe: BehindTheMedspeak: Mirror Touch Synesthesia
Symptoms Of Mirror Touch Synesthesia Transparent PNG - 768x565 - Free Download on NicePNG
What Is Mirror Touch Synesthesia? | Betterhelp
What Is Mirror-Touch Synesthesia? Scientists Probe Rare Brain Wiring
Mirror-Touch Synesthesia - A Way to Connect - Exploring your mind
Explaining mirror-touch synesthesia
Psychology Today: Help Arrives for Mirror-Touch Synesthetes
 Researchers examine unusual condition of mirror-touch synesthesia
Researchers examine unusual condition of mirror-touch synesthesia




![PDF] Influence of the body schema on mirror-touch synesthesia | Semantic Scholar PDF] Influence of the body schema on mirror-touch synesthesia | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/15f3c5fab54d3010ec9ad9aff5199fa95e429181/9-Figure5-1.png)





























Posting Komentar untuk "mirror touch synesthesia"