Carotid Cavernous Fistula Treatment
Carotid cavernous fistula treatment. The goal of endovascular embolization is to cause thrombosis of the fistula while preserving the patency of the internal carotid artery. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Treatment. As a result the blood can drain properly from the eyes.
Agents include detachable coils or liquid embolic agents delivered transarterially or transvenously. In most instances endovascular treatment is preferredHigh-flow direct CCFs usually are traumatic or are caused by rupture of a cavernous aneurysm into the sinus but a small percentage can be spontaneous. This too is rarely indicated.
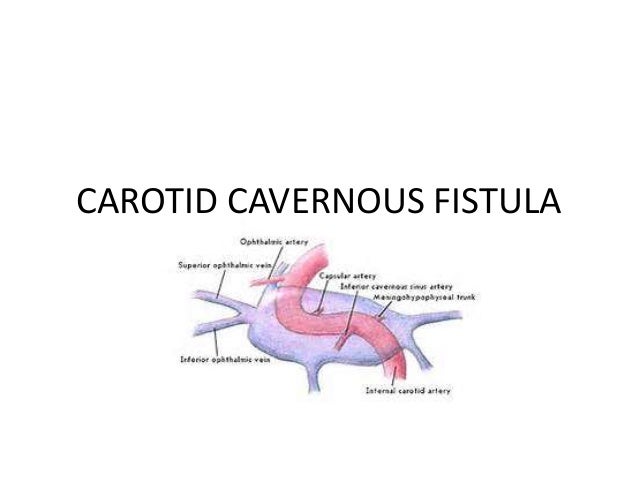
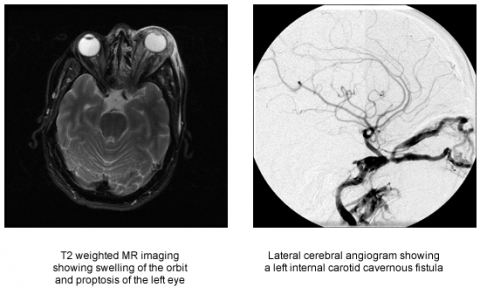
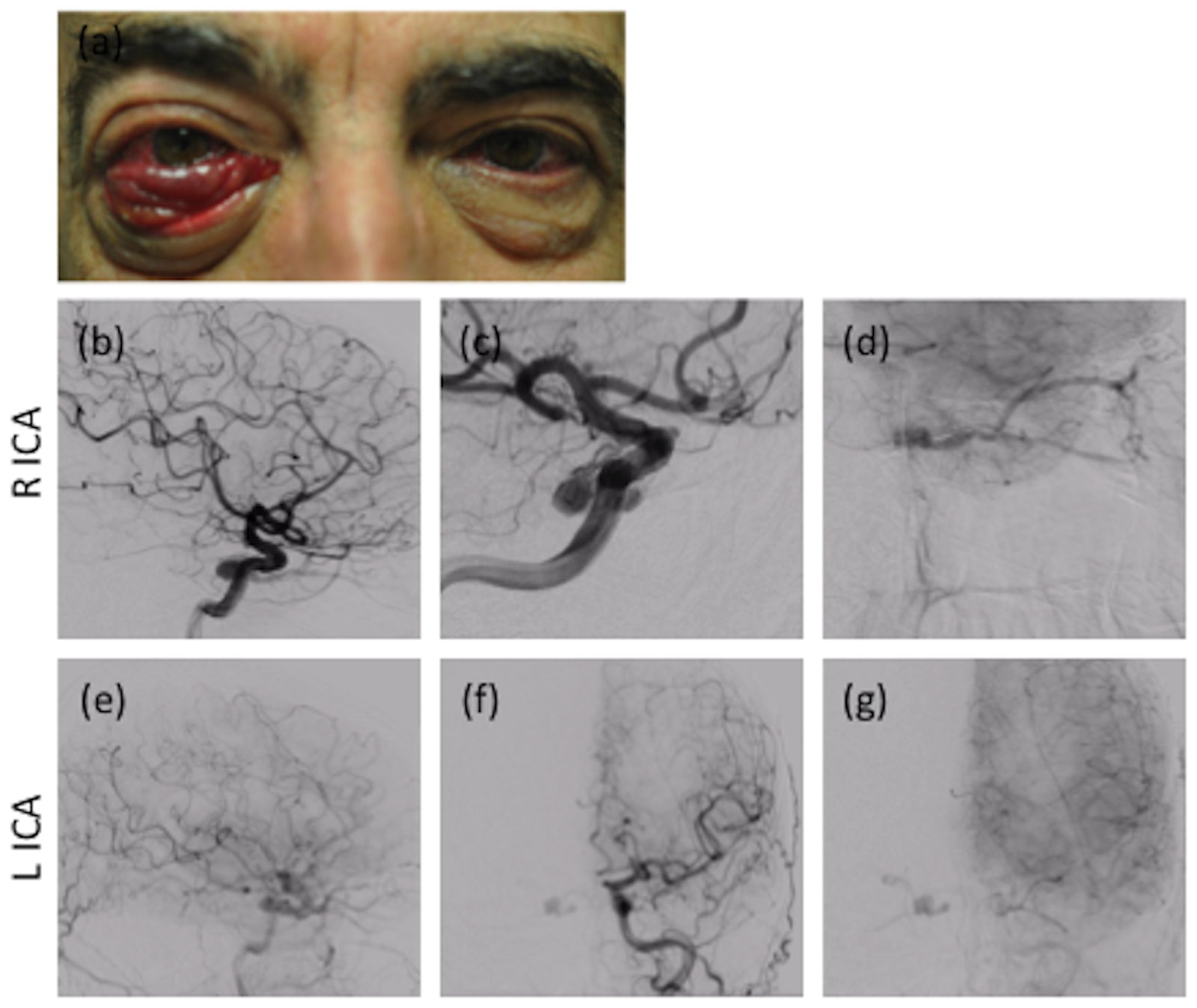
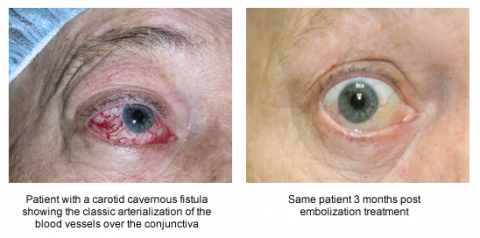
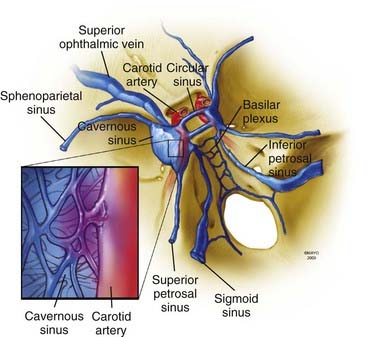
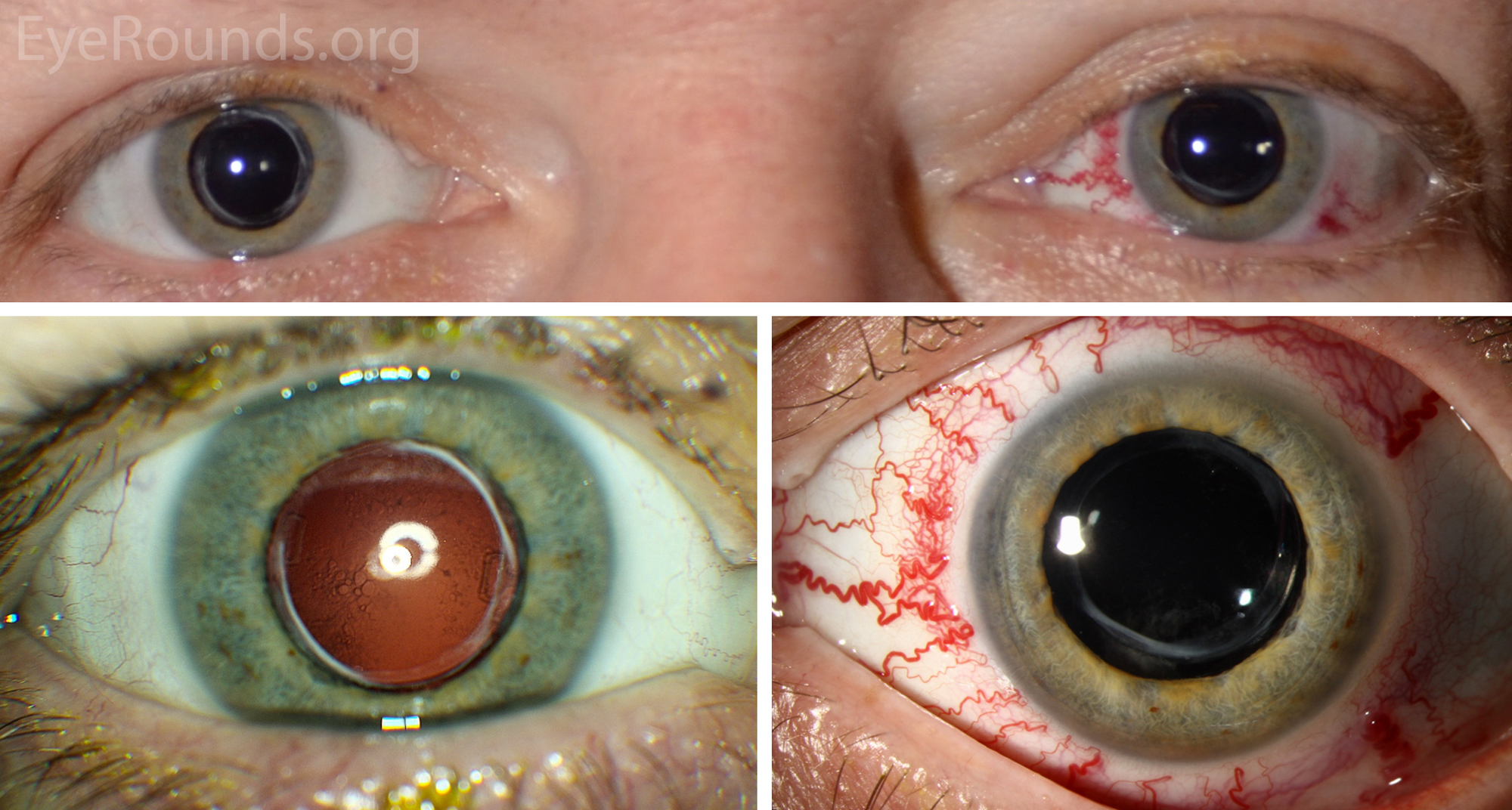
It is a type of arteriovenous fistulaAs arterial blood under high pressure enters the cavernous sinus the normal venous return to the cavernous sinus is impeded and this causes engorgement of the draining veins manifesting most dramatically as a. Treatment to treat carotid-cavernous fistula depend on the type of fistula and how soon the diagnosis was made. When the fistula is hint that is to say low flow it is usually advised keep a regular medical follow-up since they usually resolve on their own and are considered a benign condition that does not undermine the patients vision.
Percutaneous transarterial embolization using detachable balloons preferred or platinum coils is considered the treatment of choice. Fortunately treatment security and success have increased drastically over the years. The treatment of a carotid cavernous fistula CCF depends on the severity of the clinical symptoms its angiographic characteristics and the risk it presents for intracranial hemorrhage.
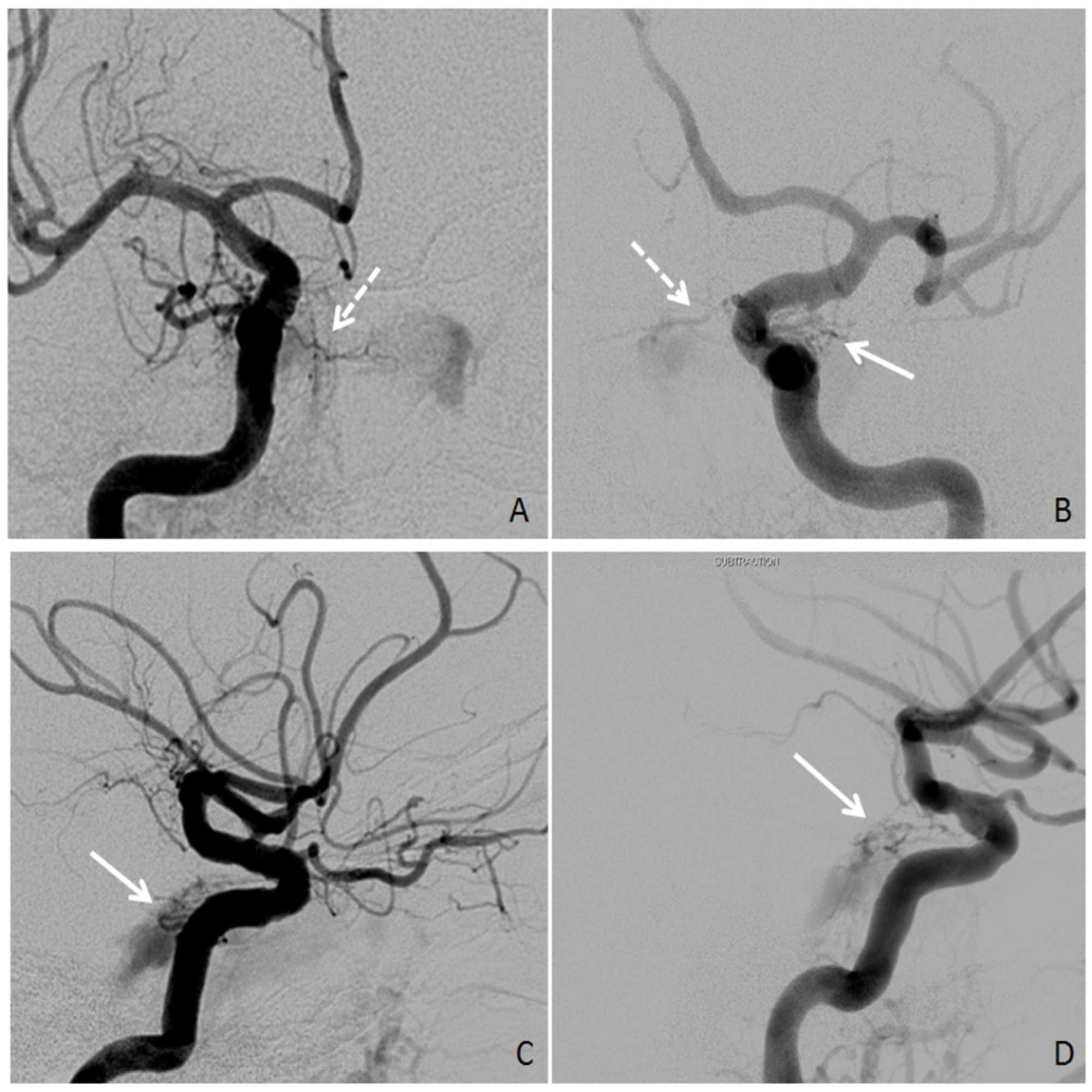
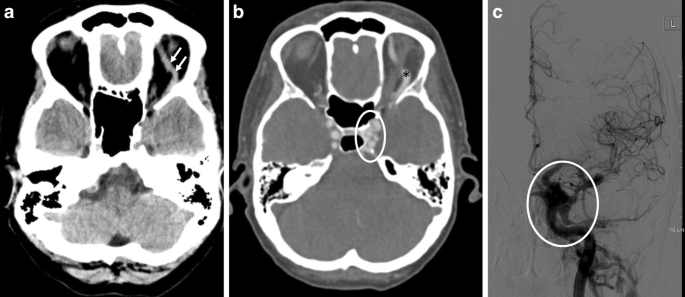
From January 1993 to December 2003 33 patients were diagnosed with CCF and treated at our hospital. Carotid cavernous sinus fistulas CCFs are abnormal communications between the carotid arterial system and the cavernous sinus. Sometimes a spontaneous fistula and a low flow fistula will get better and close on its own but its unlikely that a direct fistula will.
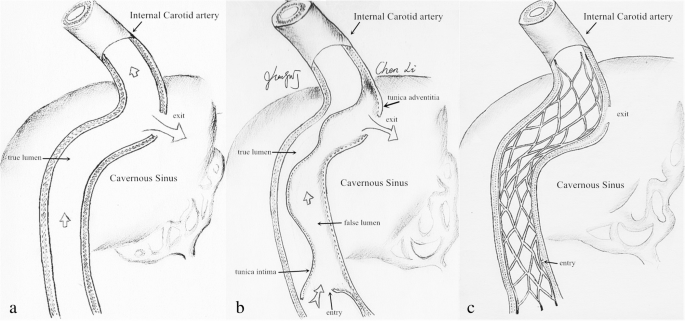
Treatment of Carotid-Cavernous Sinus Fistula In some cases an indirect CCF will close without any treatment. If IOP stays significantly elevated closure of the fistula is the best treatment. The types of treatment for direct carotid cavernous fistula dCCF have been gradually developed from early internal carotid artery ICA occlusion and balloon embolism to the present detachable coil combined with Onyx covered stent treatment.
Close hole keep the artery open. Recent advances in endovascular techniques have resulted in several therapeutic modalities becoming available and the endovascular approach has evolved as the primary treatment option for the management of CCFs.
Percutaneous transarterial embolization using detachable balloons preferred or platinum coils is considered the treatment of choice.
Carotid cavernous sinus fistulas CCFs are abnormal communications between the carotid arterial system and the cavernous sinus. Intraocular surgery to control secondary glaucoma or unrelated cataract carries a high threat since of the orbital venous hypertension. This too is rarely indicated. The treatment of a carotid cavernous fistula CCF depends on the severity of the clinical symptoms its angiographic characteristics and the risk it presents for intracranial hemorrhage. This study aims to assess the safety and efficacy of the modified treatment through point-to-point coil embolization of direct carotid cavernous fistula dCCF and evaluate the long-term outcome of patients who underwent the above treatment. Direct CCFs are always treated with endovascular methods. Sometimes a spontaneous fistula and a low flow fistula will get better and close on its own but its unlikely that a direct fistula will. The types of treatment for direct carotid cavernous fistula dCCF have been gradually developed from early internal carotid artery ICA occlusion and balloon embolism to the present detachable coil combined with Onyx covered stent treatment. Agents include detachable coils or liquid embolic agents delivered transarterially or transvenously.
Close hole keep the artery open. To evaluate the results of the treatment of 33 patients with carotid-cavernous fistula CCF with respect to clinical and angiographic criteria. If IOP stays significantly elevated closure of the fistula is the best treatment. The treatment of a carotid cavernous fistula CCF depends on the severity of the clinical symptoms its angiographic characteristics and the risk it presents for intracranial hemorrhage. Percutaneous transarterial embolization using detachable balloons preferred or platinum coils is considered the treatment of choice. Close hole keep the artery open. It is a type of arteriovenous fistulaAs arterial blood under high pressure enters the cavernous sinus the normal venous return to the cavernous sinus is impeded and this causes engorgement of the draining veins manifesting most dramatically as a.






























Posting Komentar untuk "Carotid Cavernous Fistula Treatment"