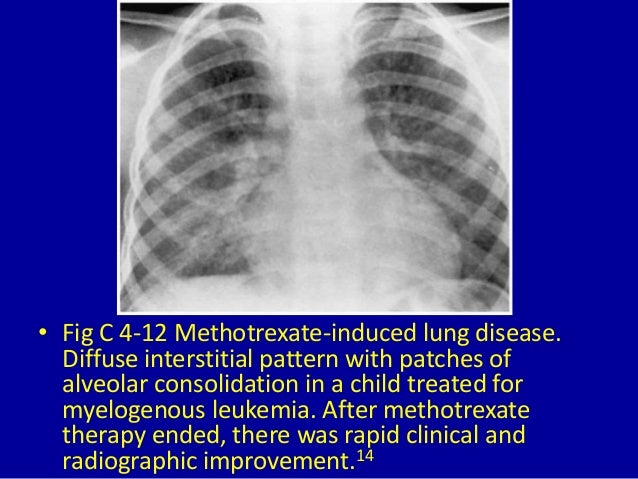
Methotrexate Induced Lung Disease
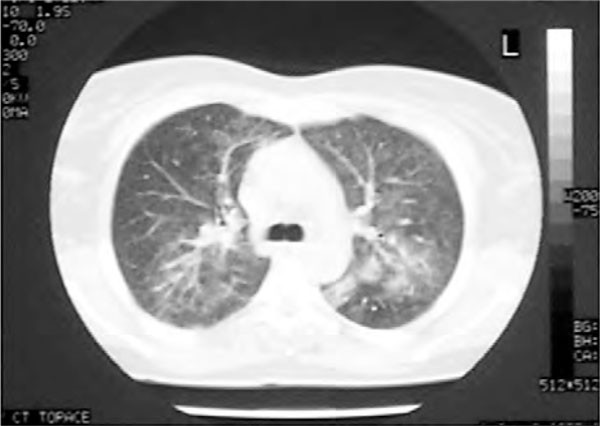
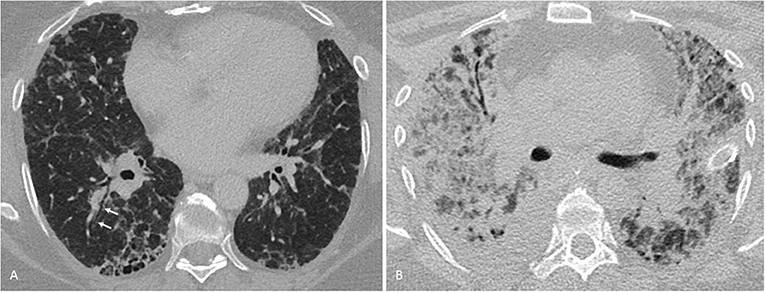
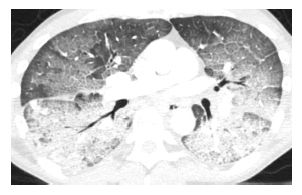
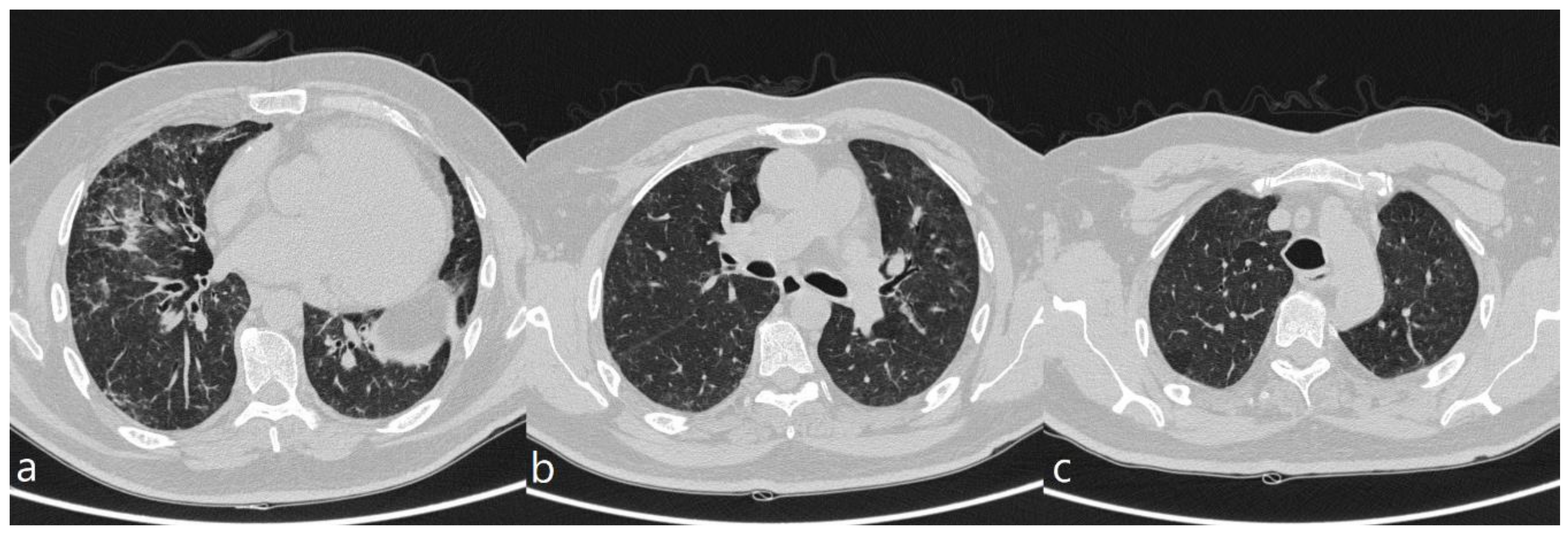
Methotrexate induced lung disease. Lavage fluid was characterised by the presence of large numbers of lymphocytes which in two patients were predominantly lymphocytes of the T8 phenotype. Fibrotic disease organising pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organising pneumonia. The results of bronchoalveolar lavage in three patients with a presumptive diagnosis of methotrexate induced lung disease are presented.
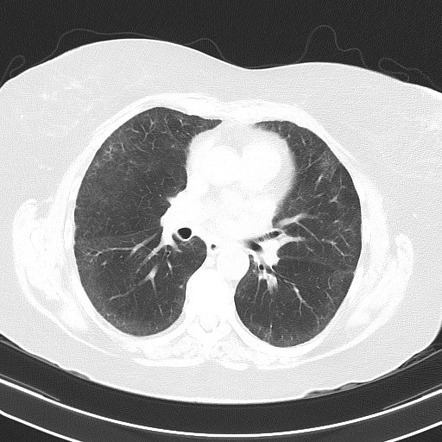
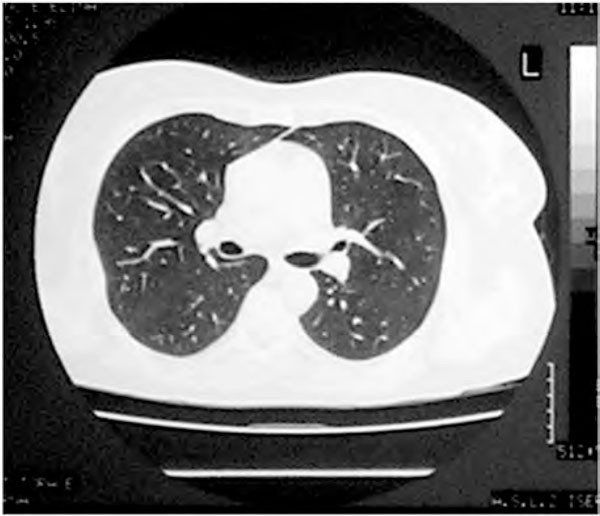
Methotrexate MTX has been described as producing an acute usually self limited pneumonitis. MTX which is the anchor-drug for the treatment of RA has been associated with lung injury and in particular with MTX-related pneumonitis M-pneu. It is used to treat a variety of malignancies connective tissue diseases and also psoriasis.
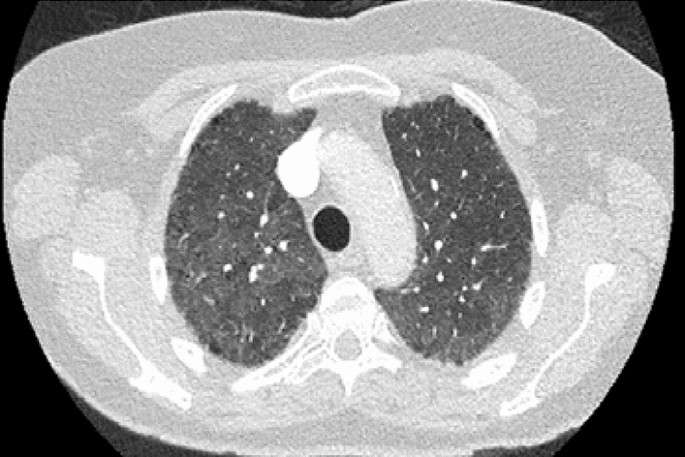
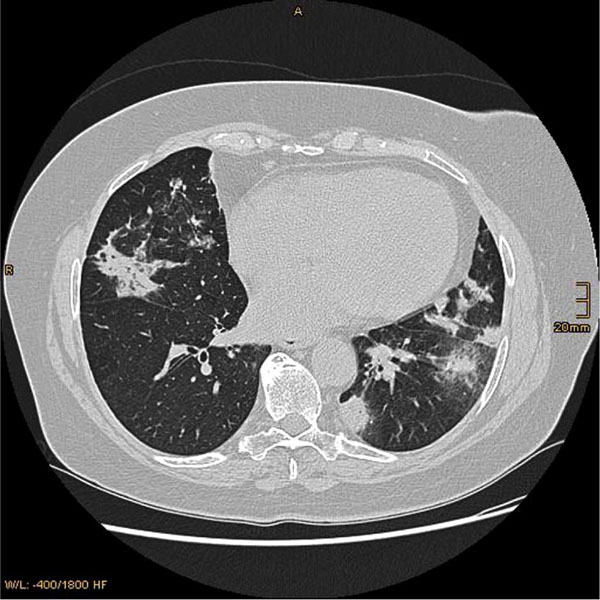
For years standard medication with Methotrexate MTX has been suspected of. Most patients with MTX-induced lung disease have a complete recovery of pulmonary function. Serious toxicity from methotrexate may affect the lungs liver and bone marrow 128-11.
32 However some patients are reported to have sustained permanent lung damage. In addition to its antiproliferative effects methotrexate has antiinflammatory and immunomodulating properties 235-7. Methotrexate-induced lung disease is a good example an entity widely believed to be common serious and potentially fatal.
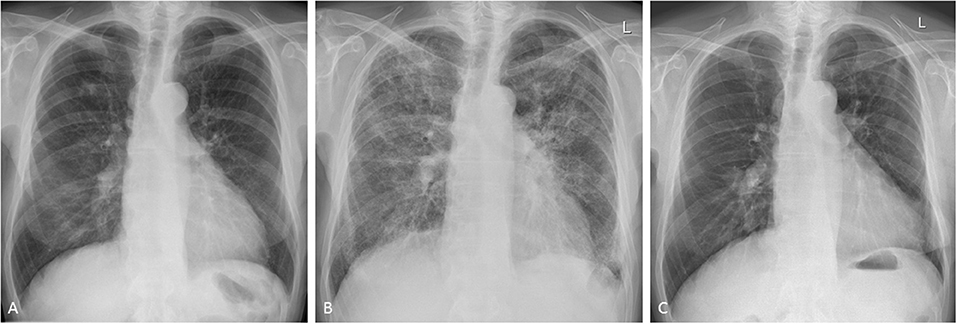
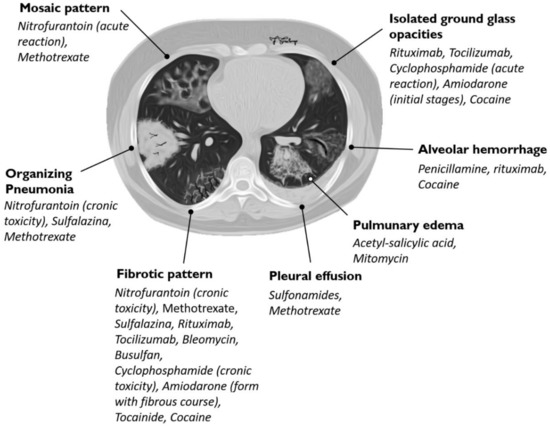
There can be several manifestations of methotrexate-related lung changes. Adverse events falling into this category include cytopenias interstitial lung disease or methotrexate pneumonitis and indeed methotrexate related liver disease. During a 6 year period 7 patients ages 11-64 among 100 treated developed methotrexate induced lung disease.
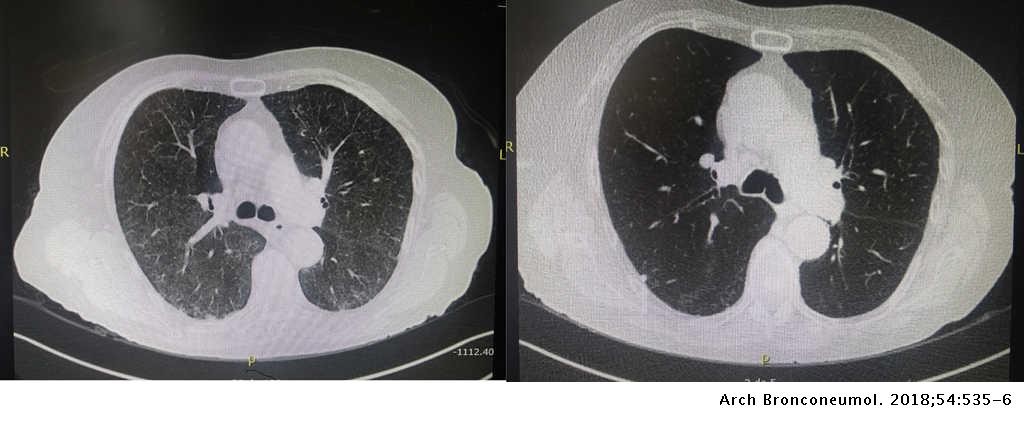
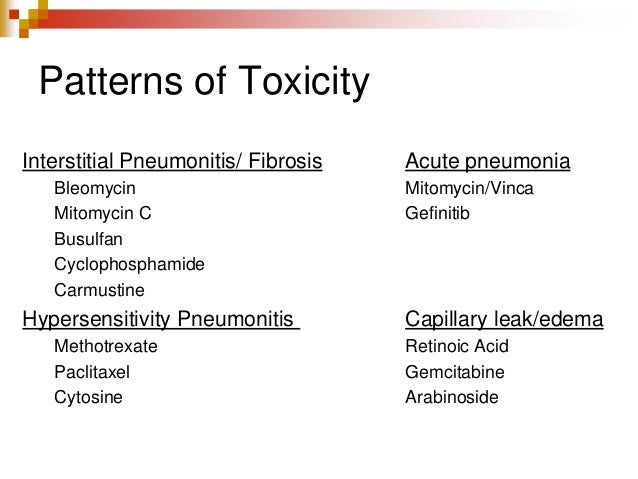
Other drug-induced lung toxicities. Distinguishing MTX-induced lung toxicity from RA-associated lung disease is vital in the clinical setting because MTX is an effective treatment of RA. Organising pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organising pneumonia or BOOP acute.
When pulmonary abnormalities are identified after an episode of MTX pneumonitis it is often difficult to know if these findings represent significant changes from baseline. Although the frequency of M-pneu has been reported to range between 03 and 116 more recent studies and meta-analyses have challenged that suggesting that it is less common than previously thought.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis RA often suffer from what is referred to as interstitial lung disease ILD.
During a 6 year period 7 patients ages 11-64 among 100 treated developed methotrexate induced lung disease. Organising pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organising pneumonia or BOOP acute. Although the frequency of M-pneu has been reported to range between 03 and 116 more recent studies and meta-analyses have challenged that suggesting that it is less common than previously thought. Fibrotic disease organising pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organising pneumonia. It is used to treat a variety of malignancies connective tissue diseases and also psoriasis. Serious toxicity from methotrexate may affect the lungs liver and bone marrow 128-11. In addition to its antiproliferative effects methotrexate has antiinflammatory and immunomodulating properties 235-7. When pulmonary abnormalities are identified after an episode of MTX pneumonitis it is often difficult to know if these findings represent significant changes from baseline. Distinguishing MTX-induced lung toxicity from RA-associated lung disease is vital in the clinical setting because MTX is an effective treatment of RA.
For years standard medication with Methotrexate MTX has been suspected of. Serious toxicity from methotrexate may affect the lungs liver and bone marrow 128-11. Lavage fluid was characterised by the presence of large numbers of lymphocytes which in two patients were predominantly lymphocytes of the T8 phenotype. Methotrexate-induced lung disease is a good example an entity widely believed to be common serious and potentially fatal. Adverse events falling into this category include cytopenias interstitial lung disease or methotrexate pneumonitis and indeed methotrexate related liver disease. Organising pneumonia formerly called bronchiolitis obliterans with organising pneumonia or BOOP acute. In addition to its antiproliferative effects methotrexate has antiinflammatory and immunomodulating properties 235-7.






























Posting Komentar untuk "Methotrexate Induced Lung Disease"