Parkinson's Disease And Basal Ganglia
Parkinson's disease and basal ganglia. Current emphasis is placed on the parallel interactions between corticostriatal and corticosubthalamic afferents on the one hand and inte. The pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease is reviewed in light of recent advances in the understanding of the functional organization of the basal ganglia BG. If requip is no longer working anymore then go to.
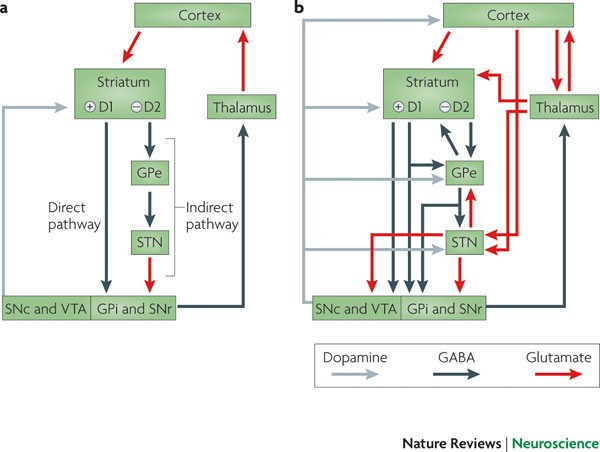
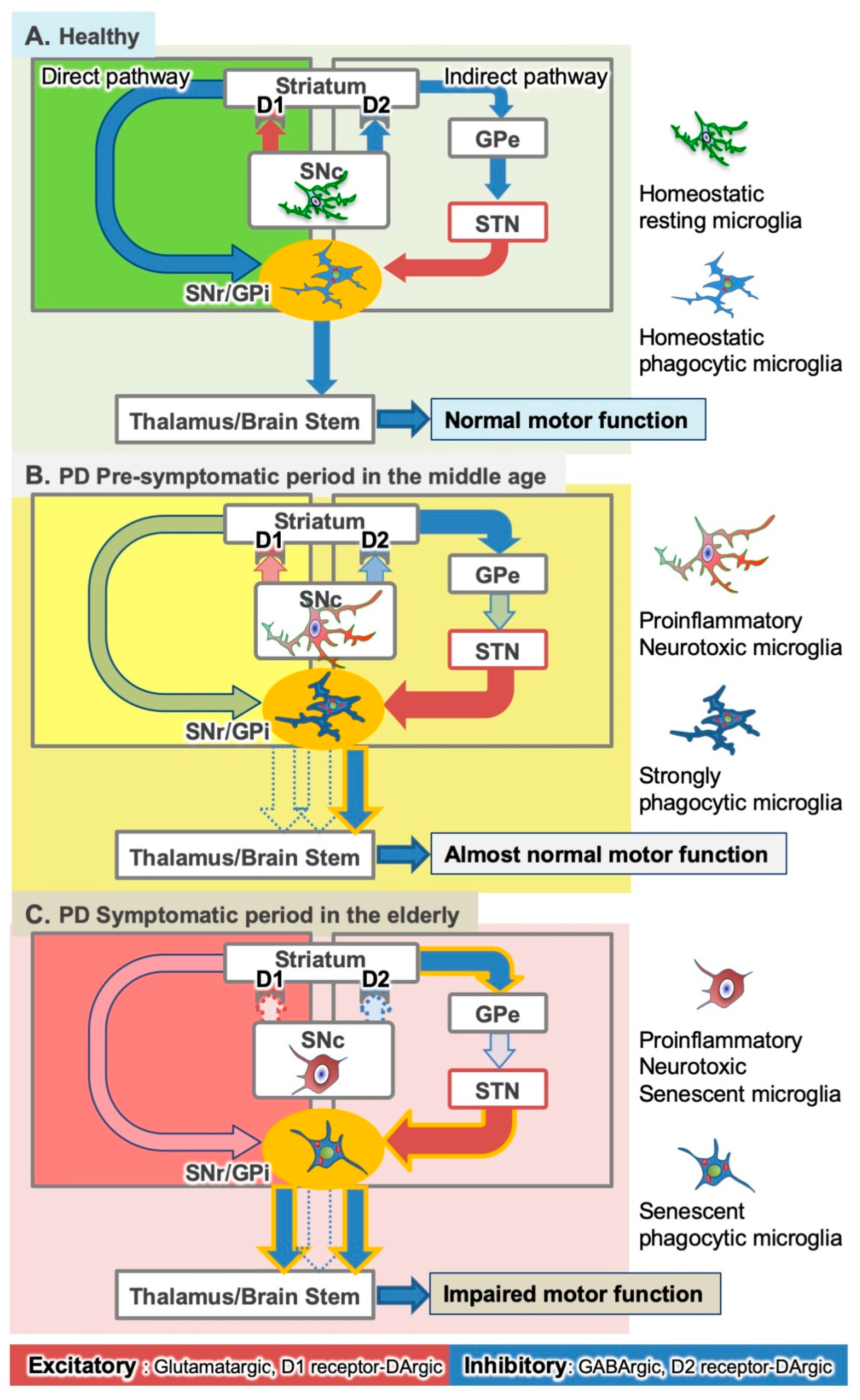
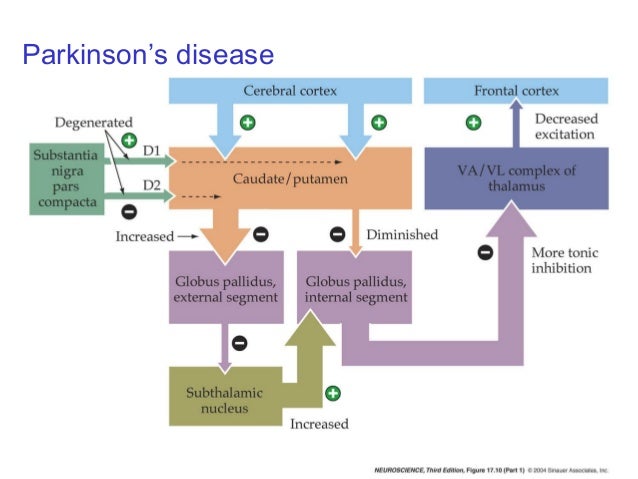
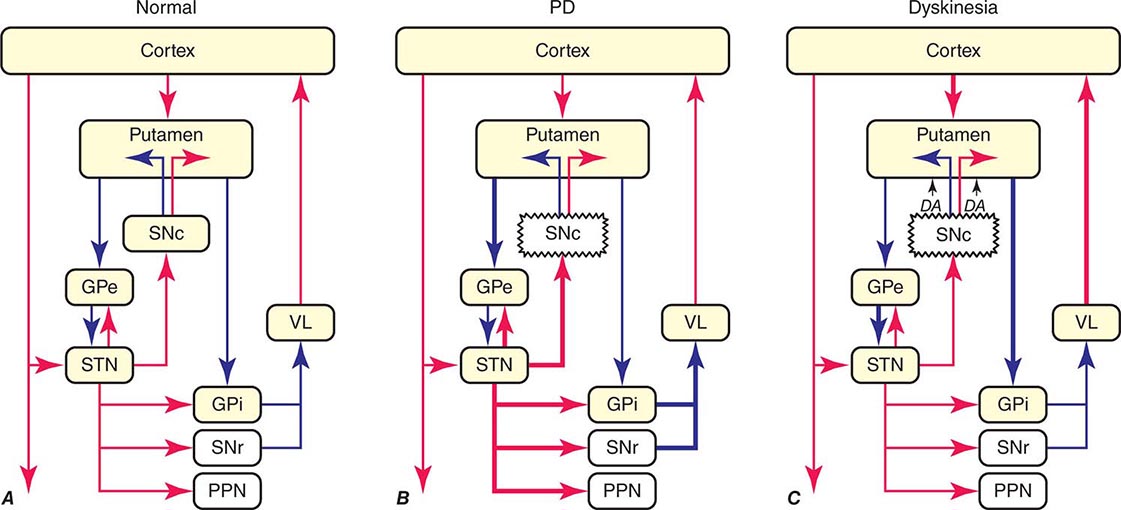
Under normal circumstances the dopamine neurons release dopamine in the basal ganglia that excites the direct pathway and inhibits the indirect pathway. In Parkinsons disease the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta triggers a cascade of functional. These ag gregates are named Lewy bodies Diagram below shows a neuronal cell on the left and red-deposits simulate the accumulation of Lewy Bodies on the.
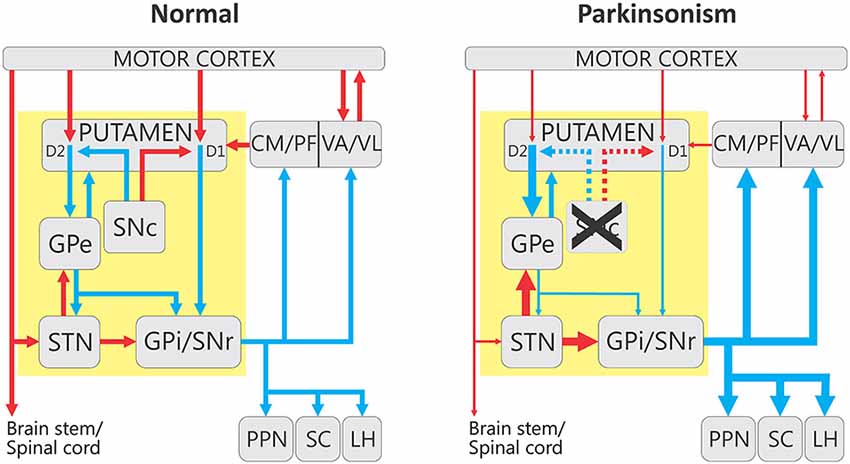
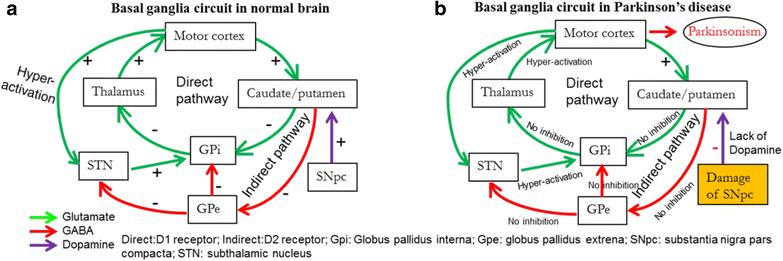
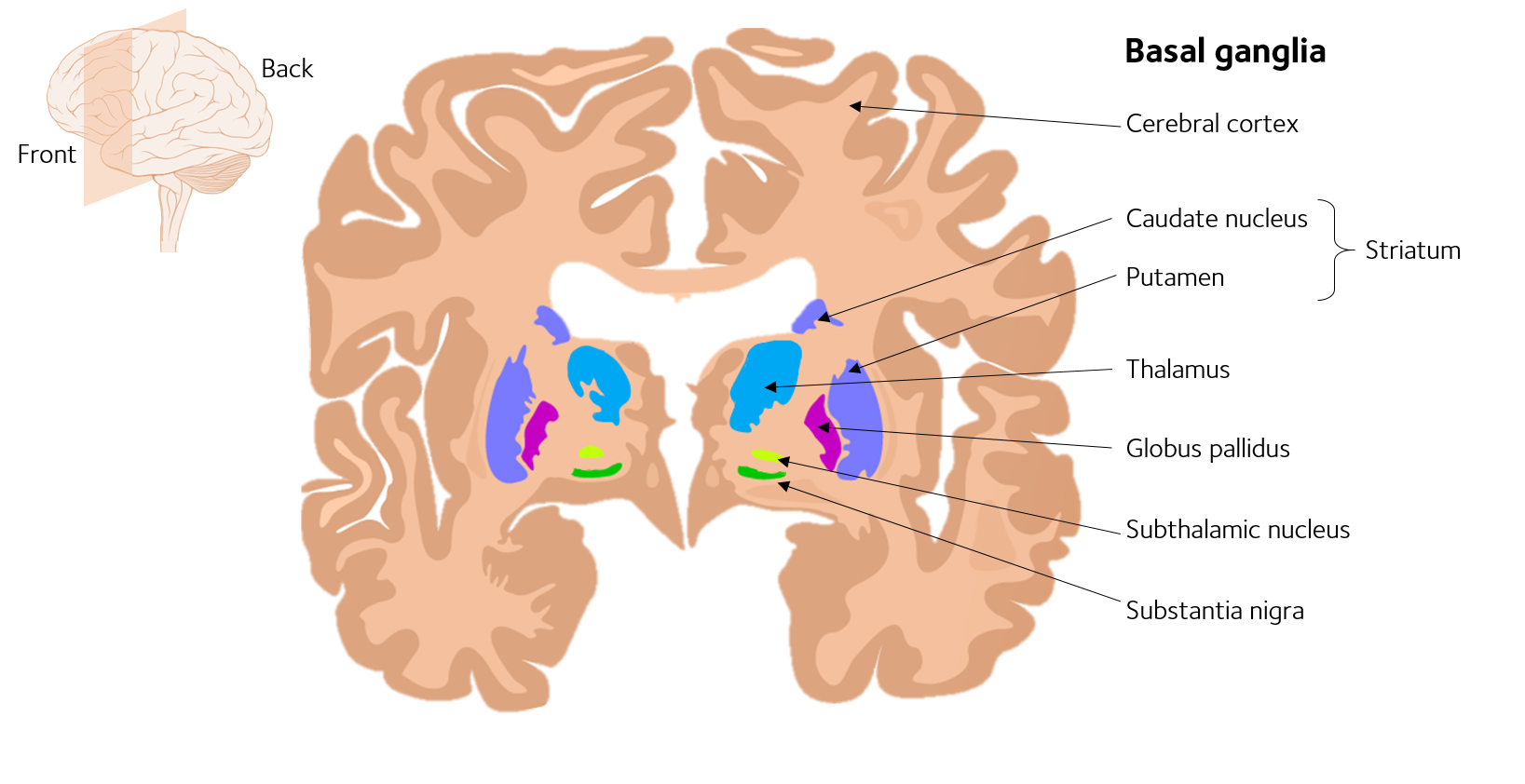
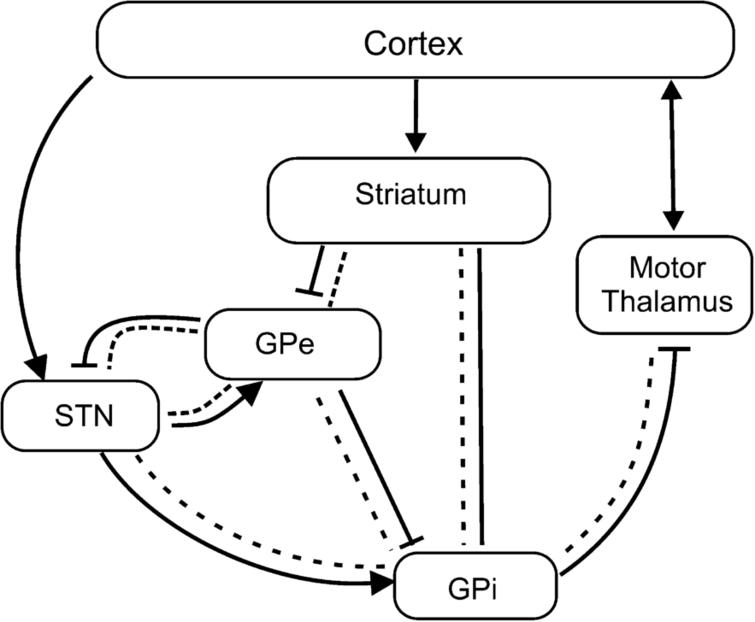
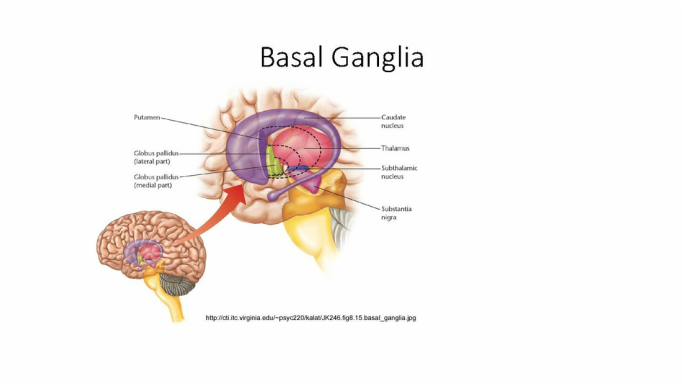
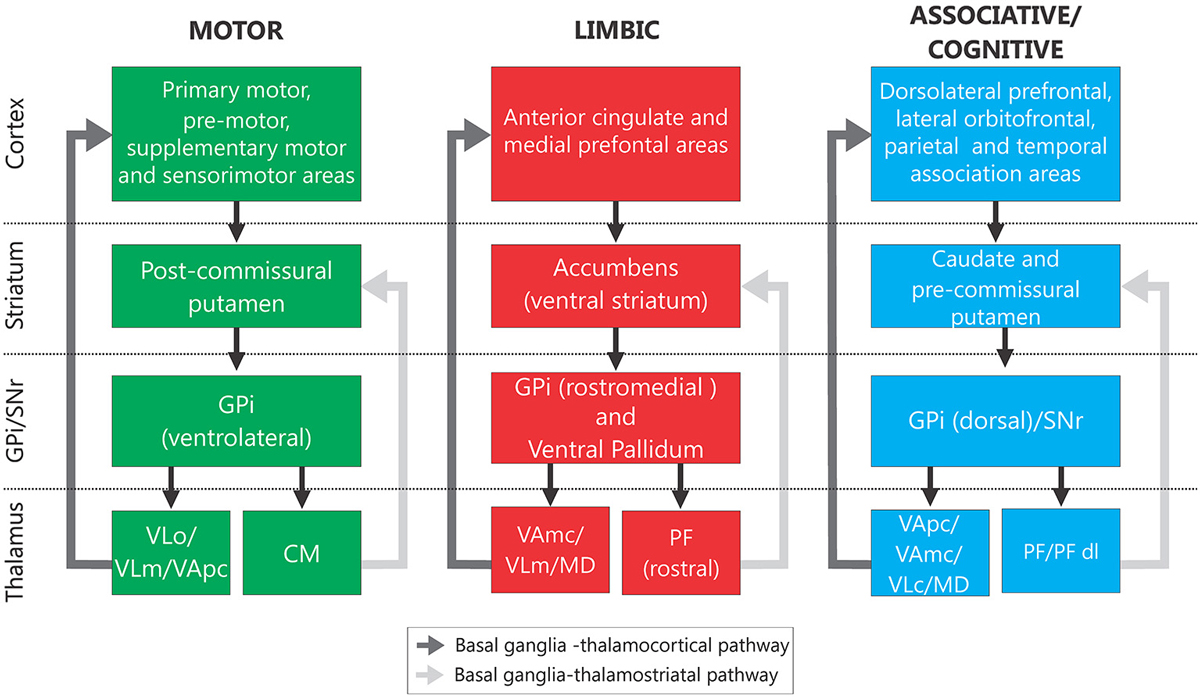
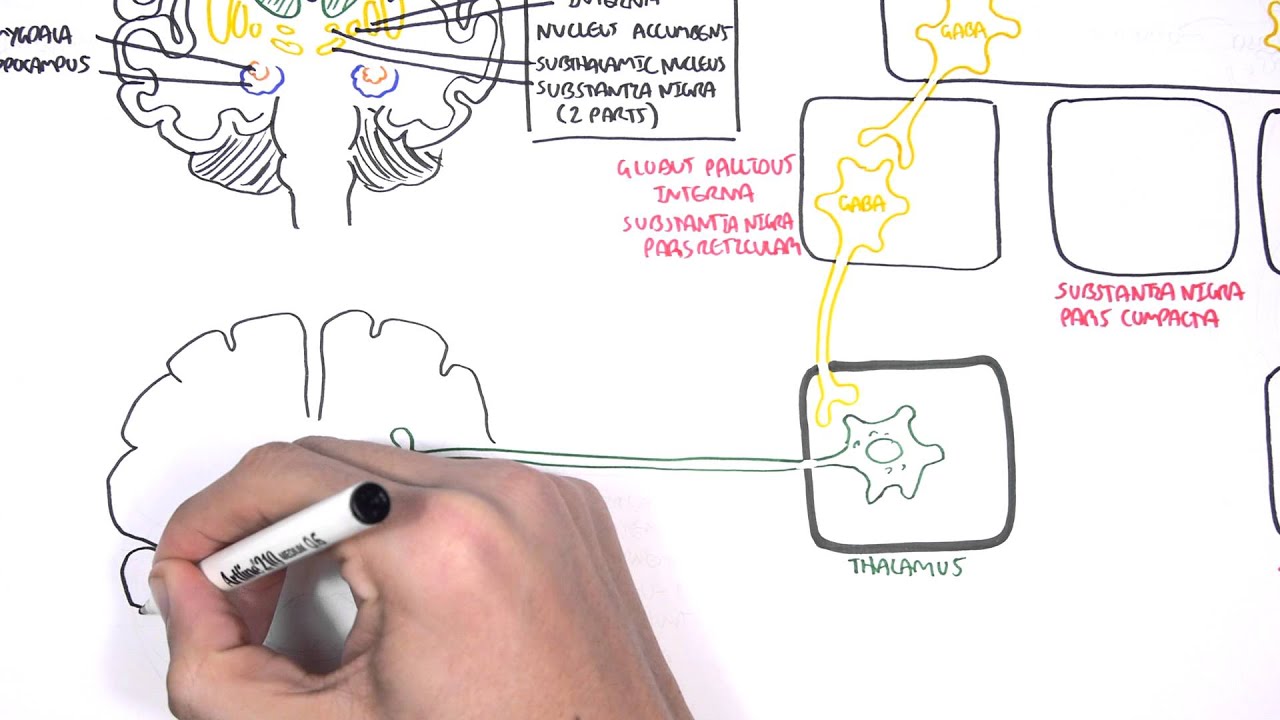
Parkinsonsdiseaseaprogressiveneurologicdisorder characterizedbytremorrigidityandslownessof movementparkinsonismwasshowninthe1960sto resultfromlossoftheneurotransmierdopamineDA withinthebasalganglia. Pathways of Basal Ganglia To understand the pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease it is necessary to look at the circuitry of the basal ganglia Two main pathways are identified The direct and The indirect 13. The main pathological characteristics of PD are cell death in the brains basal ganglia affecting up to 70 of the dopamine-secreting neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta by the end of life.
Animal Physiology 3rd Edition. What drug do you start with when someone has Parkinsons disease. The basal ganglia circuitry processes the signals that flow from the cortex allowing the correct execution of voluntary movements.
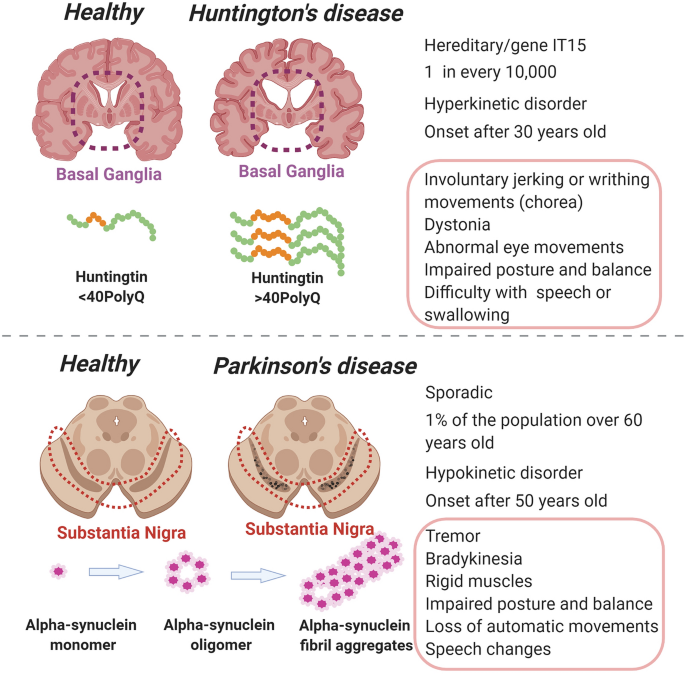
Cells are unable to remove these. Movement disorder basal ganglia cells of brain are destroyed. Parkinsons disease and Huntingtons disease are progressive neurodegenerative disorders of the basal ganglia and its connections that profoundly impact motor cognitive and psychiatric functions of affected individuals.
Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and as such many brain regions including the basal ganglia are ri. The culprit of Parkinsons is the result of alpha-synuclein accumulation and aggregation within dopaminergic neurons. Excitatory signals green and inhibitory signals red in the basal ganglia in both a normal brain and one with Parkinsons disease.
Parkinsons causes dopamine to. With the loss of dopamine neurons in Parkinsons disease however there is an increased amount of activity in the indirect pathway.
Parkinsonsdiseaseaprogressiveneurologicdisorder characterizedbytremorrigidityandslownessof movementparkinsonismwasshowninthe1960sto resultfromlossoftheneurotransmierdopamineDA withinthebasalganglia.
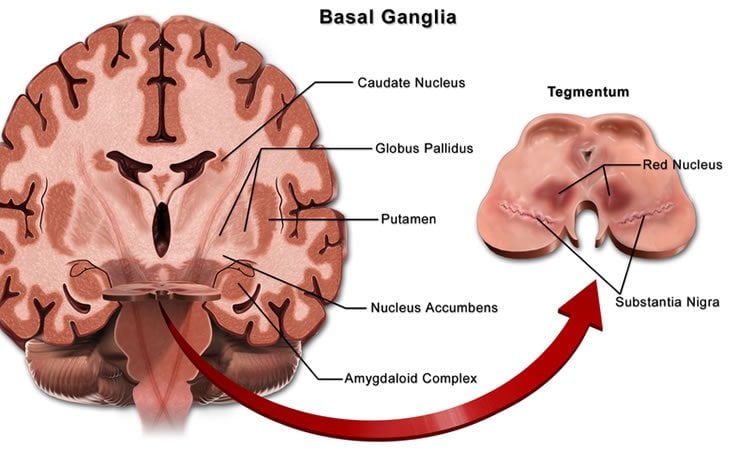
Pathways of Basal Ganglia To understand the pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease it is necessary to look at the circuitry of the basal ganglia Two main pathways are identified The direct and The indirect 13. Parkinsons disease and Huntingtons disease are progressive neurodegenerative disorders of the basal ganglia and its connections that profoundly impact motor cognitive and psychiatric functions of affected individuals. Though the numbers of people with PD in this study was small a 26-fold increased risk of Parkinsons was observed for people with ADHD compared with non-ADHD consistent with risk overall of BGC. Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system and as such many brain regions including the basal ganglia are ri. The areas of the brain involved in Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonism are called the substantia nigra and the basal ganglia. If requip is no longer working anymore then go to. The culprit of Parkinsons is the result of alpha-synuclein accumulation and aggregation within dopaminergic neurons. Parkinsons causes an imbalance of. This acts as a kind of lubricant for movement.
The pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease is reviewed in light of recent advances in the understanding of the functional organization of the basal ganglia BG. Parkinsons causes an imbalance of. Parkinsonsdiseaseaprogressiveneurologicdisorder characterizedbytremorrigidityandslownessof movementparkinsonismwasshowninthe1960sto resultfromlossoftheneurotransmierdopamineDA withinthebasalganglia. The pathophysiology of Parkinsons disease is reviewed in light of recent advances in the understanding of the functional organization of the basal ganglia BG. These ag gregates are named Lewy bodies Diagram below shows a neuronal cell on the left and red-deposits simulate the accumulation of Lewy Bodies on the. Current emphasis is placed on the parallel interactions between corticostriatal and corticosubthalamic afferents on the one hand and inte. In Parkinsons disease the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta triggers a cascade of functional.

























:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13858/Indirect_pathway.jpg)






Posting Komentar untuk "Parkinson's Disease And Basal Ganglia"